未分類
1. CLOSE_WAIT的機制和原理一.
來自參考資料:從問題看本質: 研究TCP close_wait的內幕
客戶端主動發起 socket.close時
假設我們有一個client, 一個server.
當client主動發起一個socket.close()這個時候對應TCP來說,會發生什麼事情呢?如下圖所示.
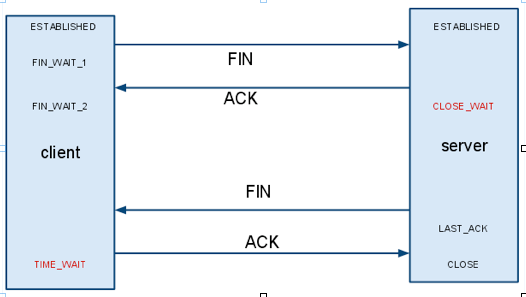
client首先發送一個FIN信號給server, 這個時候client變成了FIN_WAIT_1的狀態, server端收到FIN之後,返回ACK,然後server端的狀態變成了CLOSE_WAIT.
接著server端需要發送一個FIN給client,然後server端的狀態變成了LAST_ACK,接著client返回一個ACK,然後server端的socket就被成功的關閉了.
從這裡可以看到,如果由客戶端主動關閉一鏈接,那麼客戶端是不會出現CLOSE_WAIT狀態的.客戶端主動關閉鏈接,那麼Server端將會出現CLOSE_WAIT的狀態.
服務器端主動發起 socket.close 時
那麼當server主動發起一個socket.close(),這個時候又發生了一些什麼事情呢.
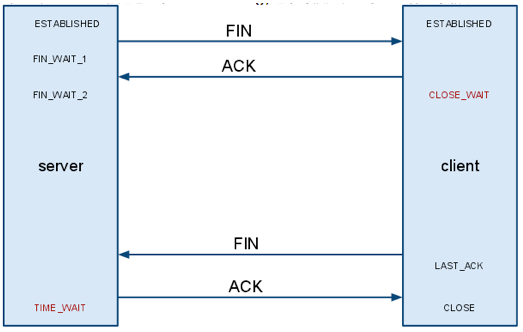
從圖中我們可以看到,如果是server主動關閉鏈接,那麼Client則有可能進入CLOSE_WAIT,如果Client不發送FIN包,那麼client就一直會處在CLOSE_WAIT狀態(後面我們可以看到有參數可以調整這個時間).
結論
誰主動關閉鏈接,則對方則可能進入CLOSE_WAIT狀態,除非對方達到超時時間,主動關閉。
服務器端的設置
如果我們的tomcat既服務於瀏覽器,又服務於其他的APP,而且我們把connection的keep-alive時間設置為10分鐘,那麼帶來的後果是瀏覽器打開一個頁面,然後這個頁面一直不關閉,那麼服務器上的socket也不能關閉,它所佔用的FD也不能服務於其他請求.如果並發一高,很快服務器的資源將會被耗盡.新的請求再也進不來. 那麼如果把keep-alive的時間設置的短一點呢,比如15s? 那麼其他的APP來訪問這個服務器的時候,一旦這個socket, 15s之內沒有新的請求,那麼客戶端APP的socket將出現大量的CLOSE_WAIT狀態.
所以如果出現這種情況,建議將你的server分開部署,服務於browser的部署到單獨的JVM實例上,保持keep-alive為15s,而服務於架構中其他應用的功能部署到另外的JVM實例中,並且將keep-alive的時間設置的更
長,比如說1個小時.這樣客戶端APP建立的connection,如果在一個小時之內都沒有重用這條connection,那麼客戶端的socket才會進入CLOSE_WAIT的狀態.針對不同的應用場景來設置不同的keep-alive時間,可以幫助我們提高程序的性能.
2. CLOSE_WAIT的機制和原理二(附實例代碼)
來自參考資料:
This is strictly a violation of the TCP specification
TCP: About FIN_WAIT_2, TIME_WAIT and CLOSE_WAIT
產生機制
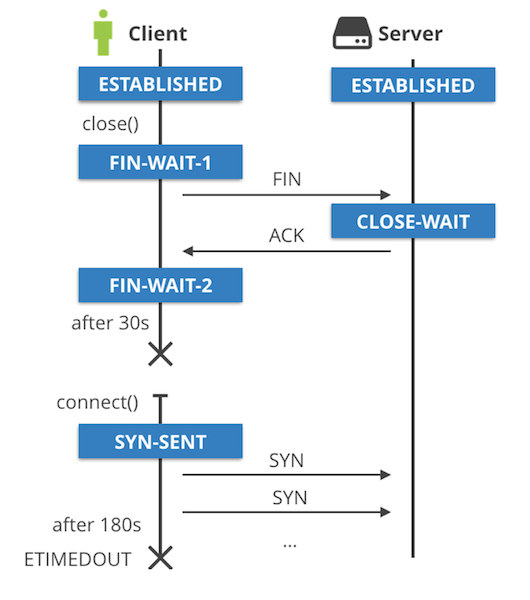
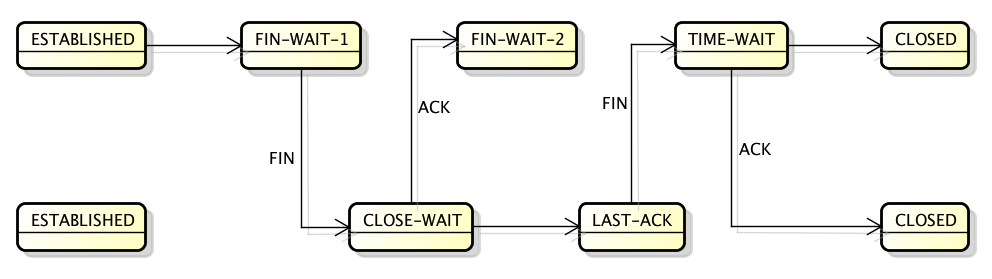
Time to raise the curtain of doubt. Here is what happens.
The listening application leaks sockets, they are stuck in CLOSE_WAIT TCP state forever. These sockets look like (127.0.0.1:5000, 127.0.0.1:some-port). The client socket at the other end of the connection is (127.0.0.1:some-port, 127.0.0.1:5000), and is properly closed and cleaned up.
When the client application quits, the (127.0.0.1:some-port, 127.0.0.1:5000) socket enters the FIN_WAIT_1 state and then quickly transitions to FIN_WAIT_2. The FIN_WAIT_2 state should move on to TIME_WAIT if the client received FIN packet, but this never happens. The FIN_WAIT_2 eventually times out. On Linux this is 60 seconds, controlled by net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout sysctl.
This is where the problem starts. The (127.0.0.1:5000, 127.0.0.1:some-port) socket is still in CLOSE_WAIT state, while (127.0.0.1:some-port, 127.0.0.1:5000) has been cleaned up and is ready to be reused. When this happens the result is a total mess. One part of the socket won’t be able to advance from the SYN_SENT state, while the other part is stuck in CLOSE_WAIT. The SYN_SENT socket will eventually give up failing with ETIMEDOUT.
sysctl -a |grep ipv4 |grep timeoutkernel.hung_task_timeout_secs = 120net.ipv4.route.gc_timeout = 300net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 60net.ipv4.tcp_thin_linear_timeouts = 0
實例問題代碼
// This is a trivial TCP server leaking sockets.package mainimport ("fmt""net""time")func handle(conn net.Conn) {defer conn.Close()for {time.Sleep(time.Second)}}func main() {IP := ""Port := 5000listener, err := net.Listen("tcp4", fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", IP, Port))if err != nil {panic(err)}i := 0for {if conn, err := listener.Accept(); err == nil {i += 1if i < 800 {go handle(conn)} else {conn.Close()}} else {panic(err)}}}
重現CLOSE_WAIT
啟動服務端
# go build listener.go && ./listener &# ss -n4tpl 'sport = :5000'State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:PortLISTEN 0 128 *:5000 *:* users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=3))
啟動客戶端,用nc
ss -n4tpl 'sport = :5000'State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:PortLISTEN 0 128 *:5000 *:* users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=3))ESTAB 0 0 127.0.0.1:5000 127.0.0.1:47810 users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=5))
可以看到啟動了一個socket連接,客戶端端口是47810.
殺死客戶端
kill `pidof nc`
服務端連接進入CLOSE_WAIT.
ss -n4tp |grep 5000CLOSE-WAIT 1 0 127.0.0.1:5000 127.0.0.1:47810 users:(("listener",pid=15158,fd=5))
TCP設計說明
It seems that the design decisions made by the BSD Socket API have unexpected long lasting consequences. If you think about it – why exactly the socket can automatically expire the FIN_WAIT state, but can’t move off from CLOSE_WAIT after some grace time. This is very confusing… And it should be! The original TCP specification does not allow automatic state transition after FIN_WAIT_2 state! According to the spec FIN_WAIT_2 is supposed to stay running until the application on the other side cleans up.
Let me leave you with the tcp(7) manpage describing the tcp_fin_timeout setting:
tcp_fin_timeout (integer; default: 60)This specifies how many seconds to wait for a final FIN packet before the socket is forcibly closed. This is strictly a violation of the TCP specification, but required to preventdenial-of-service attacks.
I think now we understand why automatically closing FIN_WAIT_2 is strictly speaking a violation of the TCP specification.
3. CLOSE_WAIT 處理說明
如果您發現與給定進程相關的連接往往總是處於CLOSE_WAIT狀態,則意味著此進程在被動關閉後不執行活動關閉。編寫通過TCP進行通信的程序時,應檢測遠程主機何時關閉連接並正確關閉套接字。如果您未能執行此操作,則套接字將保留在CLOSE_WAIT中,直到進程本身消失。
所以基本上,CLOSE_WAIT意味著操作系統知道遠程應用程序已關閉連接並等待本地應用程序也這樣做。因此,您不應嘗試調整TCP參數來解決此問題,但請檢查擁有本地主機上的連接的應用程序。由於沒有CLOSE_WAIT超時,連接可以永遠保持這種狀態(或者至少在程序最終關閉連接或進程存在或被殺死之前)。
如果您無法修復應用程序或修復它,解決方案是終止打開連接的進程。當然,由於本地端點仍然可以在緩衝區中發送數據,因此仍然存在丟失數據的風險。此外,如果許多應用程序在同一進程中運行(就像Java Enterprise應用程序的情況一樣),那麼終止擁有進程並不總是一種選擇。
我沒有嘗試使用tcpkill,killcx或者cutter強制關閉CLOSE_WAIT連接但是如果你不能殺死或重啟持有連接的進程,那麼它可能是一個選項。
4. 查看CLOSE_WAIT的ip與端口連接對
netstat -tulnap | grep CLOSE_WAIT | sed -e 's/::ffff://g' | awk '{print $4,$5}' | sed 's/:/ /g'
結果舉例:
172.26.59.197 8088 54.241.136.34 44690172.26.59.197 8088 171.48.17.77 47220172.26.59.197 8088 54.241.136.34 57828172.26.59.197 8088 157.230.119.239 55920172.26.59.197 8088 157.230.119.239 59650172.26.59.197 8088 157.230.119.239 44418172.26.59.197 8088 157.230.119.239 47634172.26.59.197 8088 157.230.119.239 34940
每一行是一對CLOSE_WAIT的socket連接。示例是服務器端的連接。
5. 殺死 CLOSE_WAIT的perl代碼
源代碼:
https://github.com/rghose/kill-close-wait-connections/blob/master/kill_close_wait_connections.pl
apt-get install libnet-rawip-perl libnet-pcap-perl libnetpacket-perlgit clone https://github.com/rghose/kill-close-wait-connections.gitcd kill-close-wait-connectionsmv kill_close_wait_connections.pl /usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connectionschmod +x /usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connections
已經將其代碼放置 http://39.106.122.67/ctorrent/kill_close_wait_connections.pl
不必通過git下載。
ubuntu 準備
apt-get install libnet-rawip-perl libnet-pcap-perl libnetpacket-perl
CentOS準備
yum -y install perl-Net-Pcap libpcap-devel perl-NetPacket curl -L http://cpanmin.us | perl - --sudo App::cpanminus cpanm Net::RawIP cpanm Net::Pcap cpanm NetPacket
安裝
wget http://39.106.122.67/ctorrent/kill_close_wait_connections.plmv kill_close_wait_connections.pl /usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connectionschmod +x /usr/bin/kill_close_wait_connections
執行
kill_close_wait_connections
6. 殺死tcp 的其他命令與說明
資料1來源
Kill an active TCP connection
https://gist.github.com/amcorreia/10204572
Kill an active TCP connection內容
Some notes on killing a TCP connection…
- https://github.com/arut/linux-tcp-drop
- http://rtomaszewski.blogspot.com/2012/11/how-to-forcibly-kill-established-tcp.html
- http://killcx.sourceforge.net
- tcpkill (part of dsniff)
- cutter
Info gathering
(remember to be root!)
lsof | awk '{ print $2; }' | sort -rn | uniq -c | sort -rn | head
lsof | grep <PID>
netstat -tonp- Killcx deps:
libnet-rawip-perllibnet-pcap-perllibnetpacket-perl - tcpkill deps:
dsniff
Motivations
CLOSE_WAIT related
- http://www.sunmanagers.org/pipermail/summaries/2006-January/007068.html
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/15912370/how-do-i-remove-a-close-wait-socket-connection
- http://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/10106/orphaned-connections-in-close-wait-state
資料2來源
Kill tcp connection with tcpkill on CentOS
https://gist.github.com/vdw/09efee4f264bb2630345
Kill tcp connection with tcpkill on CentOS 內容
Install tcpkill
yum -y install dsniff --enablerepo=epel
View connections
netstat -tnpa | grep ESTABLISHED.*sshd.
Block with ip tables
iptables -A INPUT -s IP-ADDRESS -j DROP
Kill connection
tcpkill -i eth0 -9 port 50185
Block brute forcing – iptables rules
iptables -L -niptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -i eth0 -m state --state NEW -m recent --setiptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -i eth0 -m state --state NEW -m recent --update --seconds 600 --hitcount 3 -j DROPiptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW -m recent --set --name ssh --rsourceiptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW -m recent ! --rcheck --seconds 600 --hitcount 3 --name ssh --rsource -j ACCEPTservice iptables saveservice iptables restart
7. 參考資料
從問題看本質: 研究TCP close_wait的內幕
https://www.cnblogs.com/zengkefu/p/5655016.html
This is strictly a violation of the TCP specification
https://blog.cloudflare.com/this-is-strictly-a-violation-of-the-tcp-specification/
TCP: About FIN_WAIT_2, TIME_WAIT and CLOSE_WAIT
https://benohead.com/tcp-about-fin_wait_2-time_wait-and-close_wait/
kill-close-wait-connections
https://github.com/rghose/kill-close-wait-connections
Kill an active TCP connection
https://gist.github.com/amcorreia/10204572
[命令行] curl查詢公網出口IP
https://blog.csdn.net/orangleliu/article/details/51994513